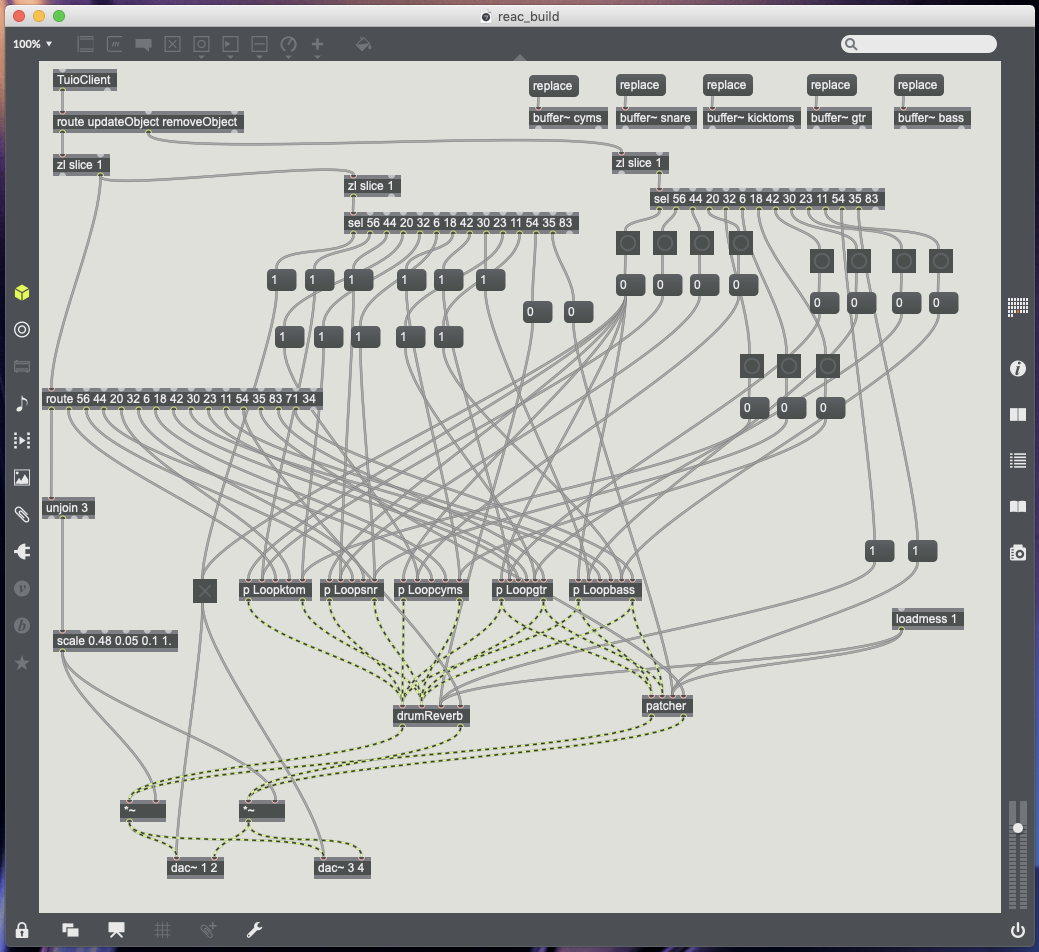
After establishing how to control different plugins using reacTIVision, the next process was to turn my table into a surface which could be used for audio mixing. The first main issue, that I encountered, was with marker placement. With the amount of markers being used, many of which work in a similar way to one another, at first using similar scale ratios, they all ended up bunching in the same area of the table. To make the best use of the tables space, also providing a ruff outline where to place markers, I marked out a basic user interface upon the clear table top (see Fig.5.1.). Once the outline of a user interface had been set, the scale objects could then be used to map the input values, relating back to a certain area of the tables surface (Cycling74, 2019).

The plugins work with the following markers in the following ways;
X floating point data (Left = 0.99 Right = 0.01).
Y floating point data (Top = 0.01 Bottom = 0.99).
Rotation floating point data (0.01 to 6.27).
Fiducial markers used;
56 – Master Control – Turns on main DAC objects, Starts playback on all buffers from 0ms (Object Update and Remove Object data) and is a master output volume control (Y data) (see Fig.5.2.).
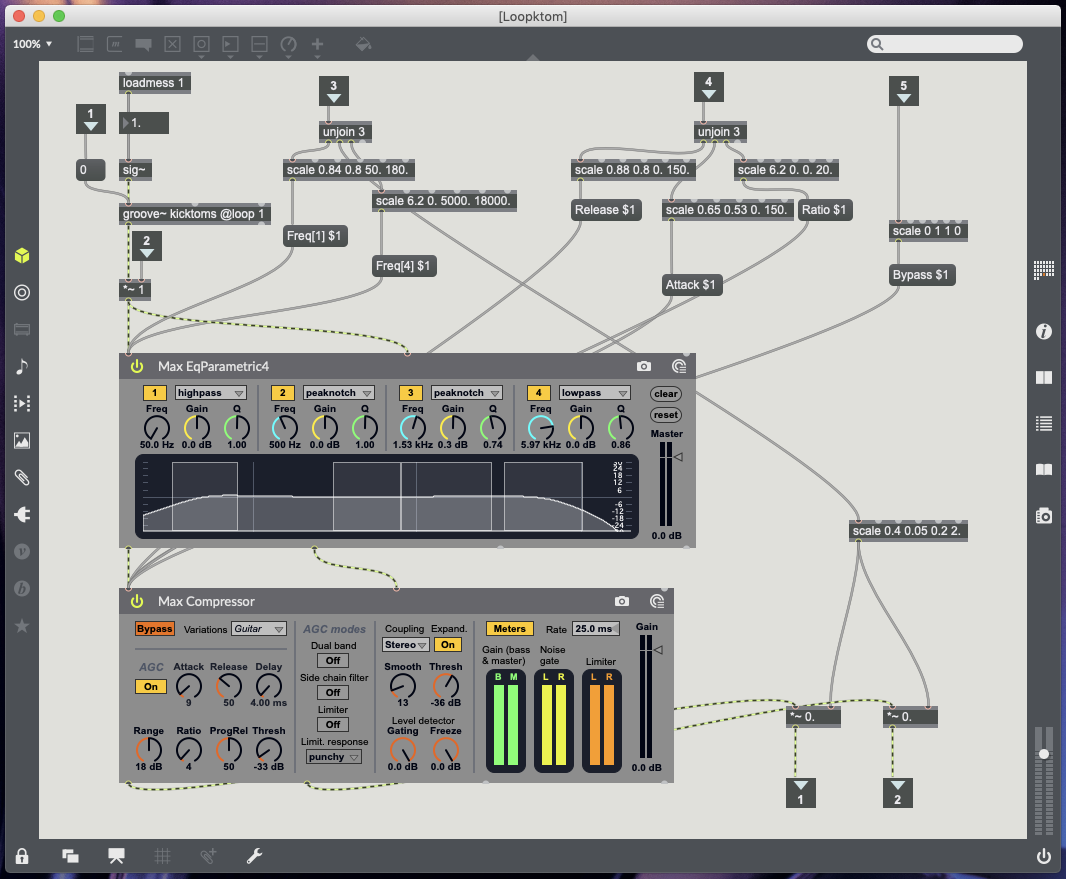
44 – Kick and Toms – Update Object sends 1 to volume to turn mute off, Remove Object sends o to volume to turn mute on (post Groove object pre plugins), X data controls high pass EQ (50Hz to 180Hz), Y data controls volume, Rotation controls low pass EQ (5000kHz to 18000kHz) (see Fig.5.3.).
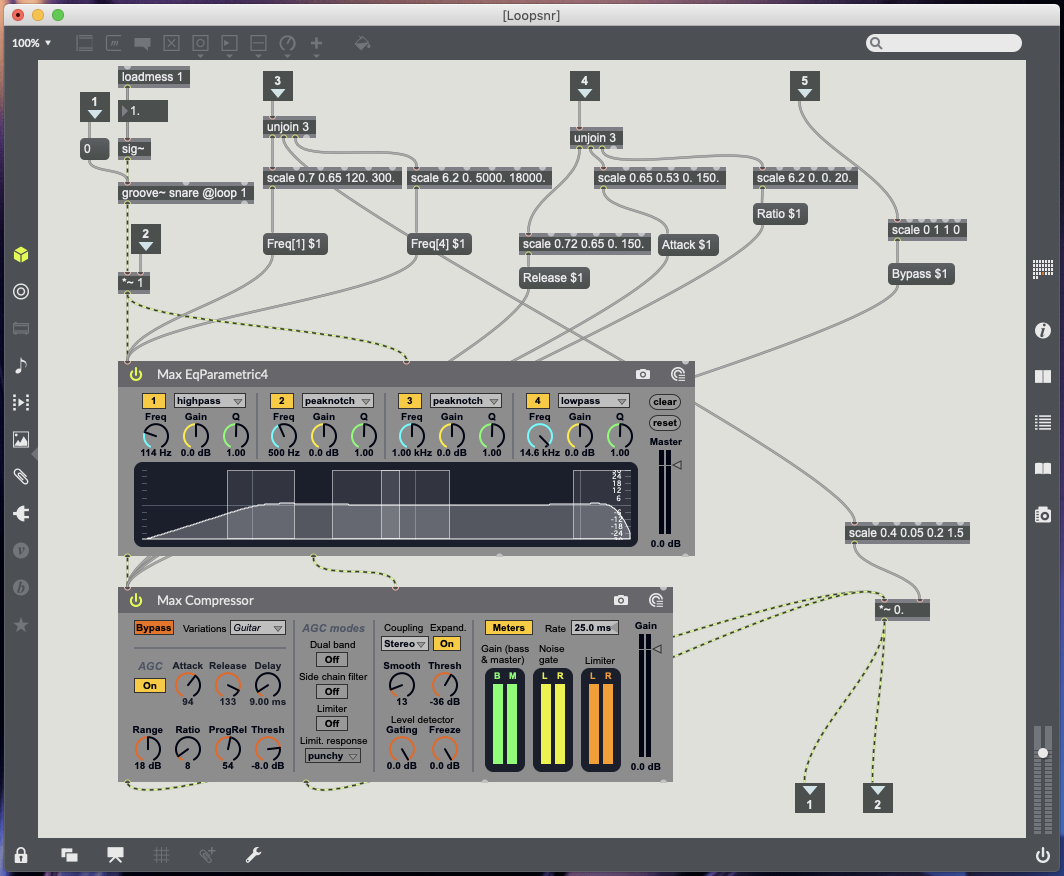
20 – Snare drum – Update Object sends 1 to volume to turn mute off, Remove Object sends o to volume to turn mute on (post Groove object pre plugins), X data controls high pass EQ (120Hz to 300Hz), Y data controls volume, Rotation controls low pass EQ (5000kHz to 18000kHz) (see Fig.5.4.).
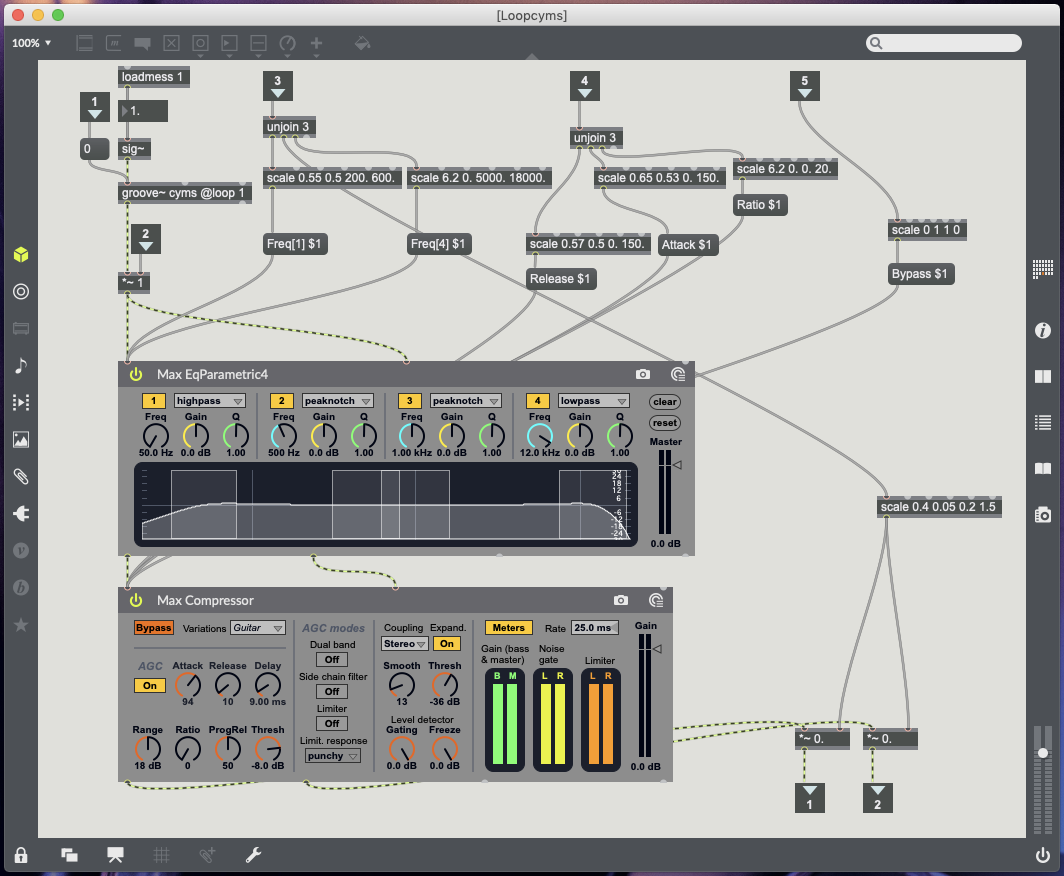
Cymbals (32) – Update Object sends 1 to volume to turn mute off, Remove Object sends o to volume to turn mute on (post Groove object pre plugins), X data controls high pass EQ (200Hz to 600Hz), Y data controls drum volume, Rotation controls low pass EQ (5000kHz to 18000kHz) (see Fig.5.5.).
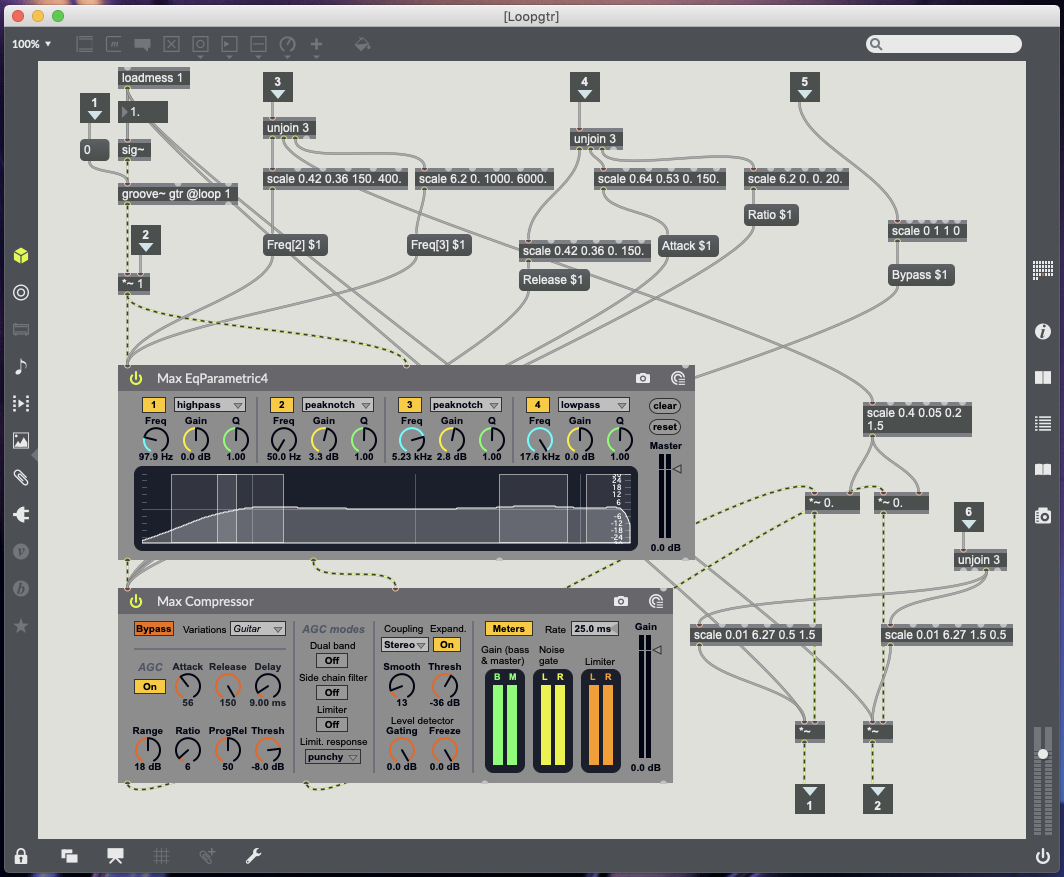
30 – Guitar – Update Object sends 1 to volume to turn mute off, Remove Object sends o to volume to turn mute on (post Groove object pre plugins), X data controls EQ peak notch (+3db) between 150Hz and 400Hz, Y data controls volume, Rotation controls EQ peak notch (+3db) between 1000kHz and 6000kHz (see Fig 5.6.).
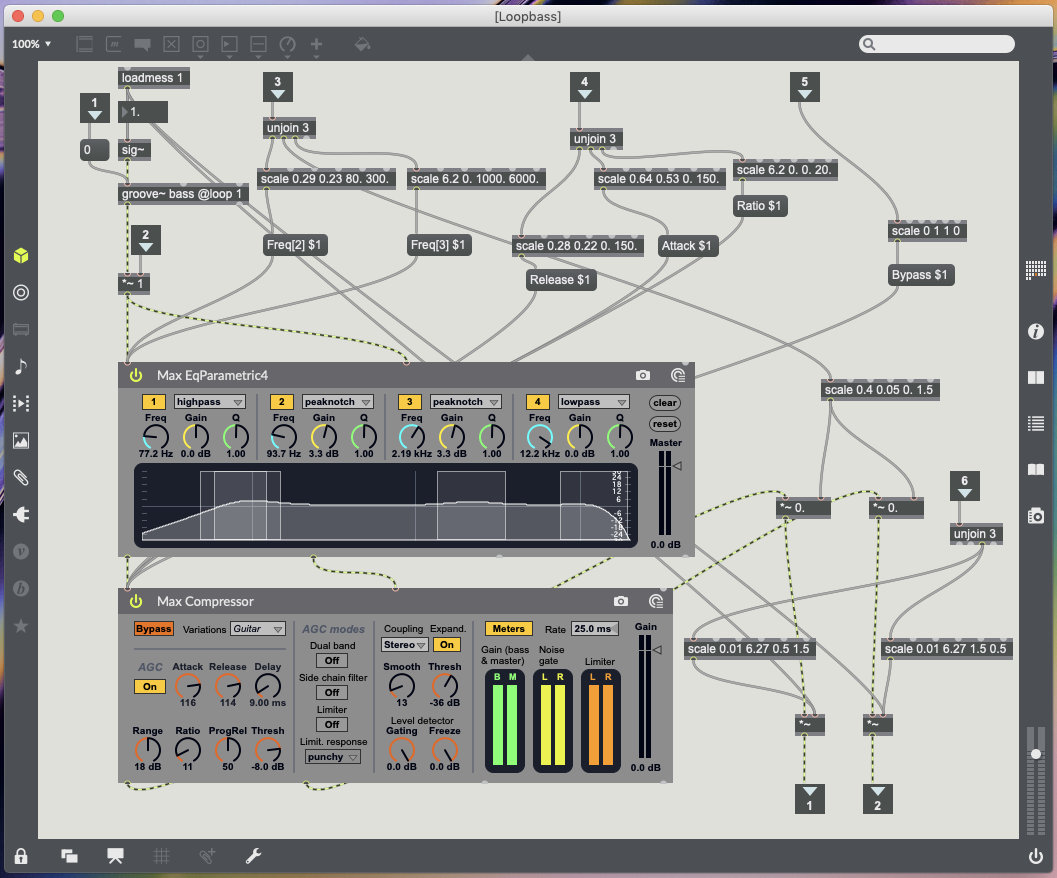
23 – Bass – Update Object sends 1 to volume to turn mute off, Remove Object sends o to volume to turn mute on (post Groove object pre plugins), X data controls EQ peak notch (+3db) between 80Hz and 300Hz, Y data controls volume, Rotation controls EQ peak notch (+3db) between 1000kHz and 6000kHz (see Fig.5.7.).
Compressor markers all work with the same movements. X data controls release time (move left for slow release time, move right for fast release time). Y data controls attack time (move to bottom for quick attack time, move to top for slow attack time). Rotation data controls ratio (Place marker facing upright with a slight tilt to the right for 0:1 ratio, keep turn right to increase ratio 20:1).
Compressor markers – 6 controls Kick & Toms (see Fig.5.3.), 18 controls Snare (see Fig.5.4.), 42 controls Cymbals (see Fig.5.5.), 11 controls Guitar (see Fig.5.6.), 54 controls Bass (see Fig.5.7.).
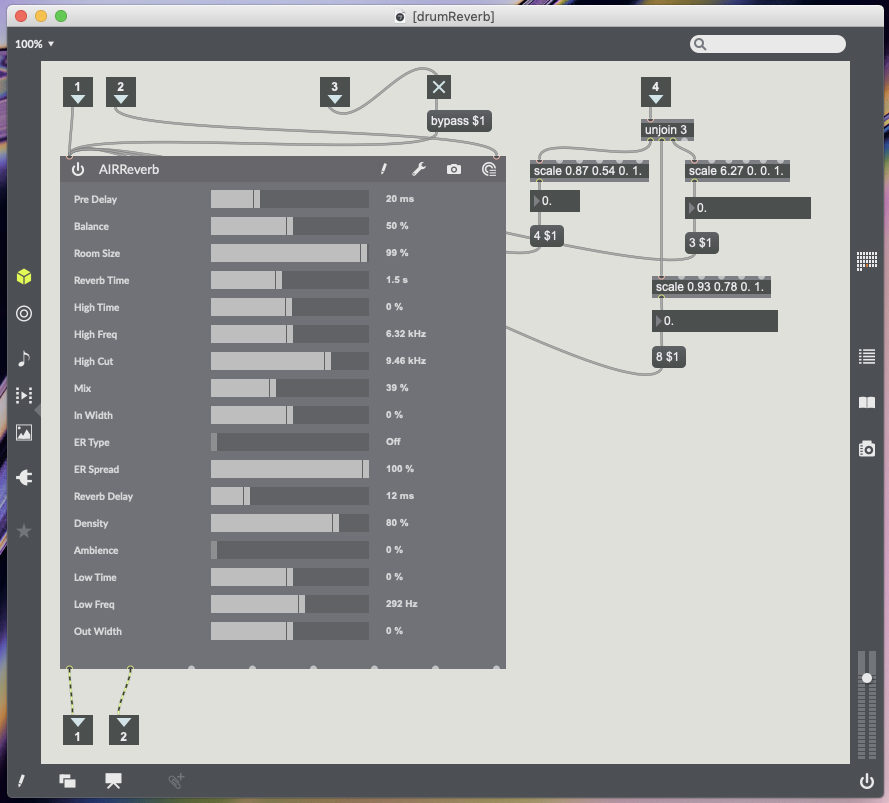
35 – Reverb Marker – Placing marker activates reverb and removing marker bypasses reverb. X data controls reverb time (Moving to the right increases reverb time left reduces reverb time). Y data controls reverb mix (Moving up increase wet/dry mix and moving down decreases wet/dry mix). Rotation data controls room size (Placing marker upright slightly to the right is smallest room size 0%, Continue turning right to increase room size 100%) (see Fig.5.8.).
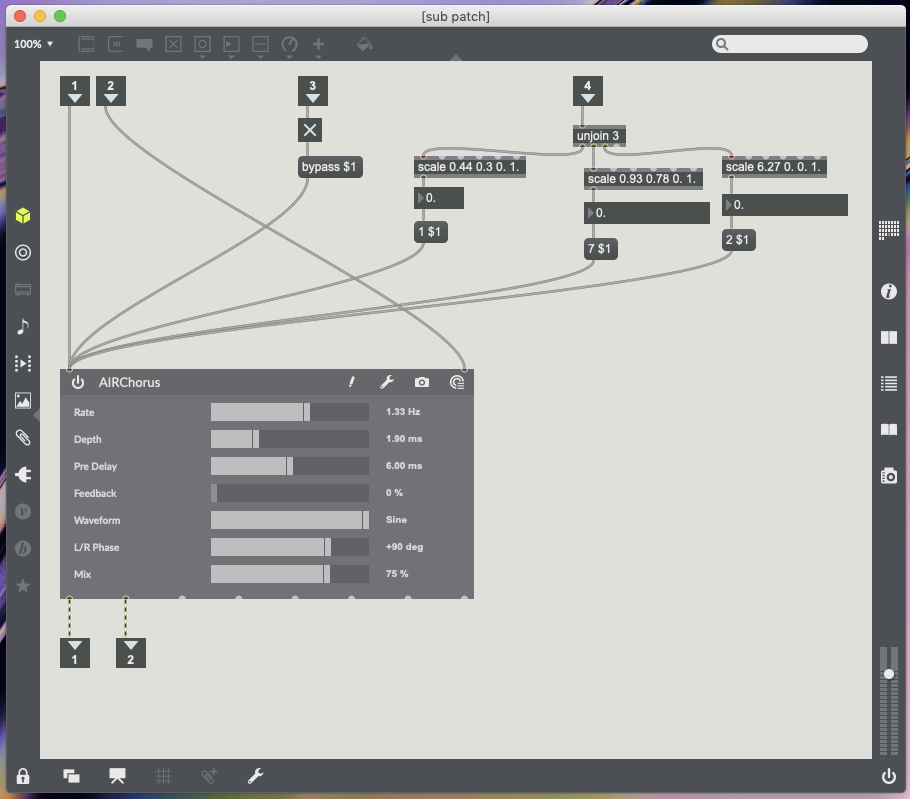
83 – Chorus marker for guitar and bass only – Placing marker activates chorus and removing marker bypasses chorus. X data controls chorus rate (Moving right increases rate and moving left decreases rate). Y data controls mix (Moving up increase chorus mix moving down decreases). Rotation data controls chorus depth (see Fig.5.9.).
71 and 34 – Instrument panning for guitar (71) and bass (34) only – These markers can be placed anywhere on the table as the only data being processed from them is the rotation data. This controls two multiplication objects so guitar and bass can be panned left and right (see Fig.5.6. for guitar and Fig.5.7. for bass).
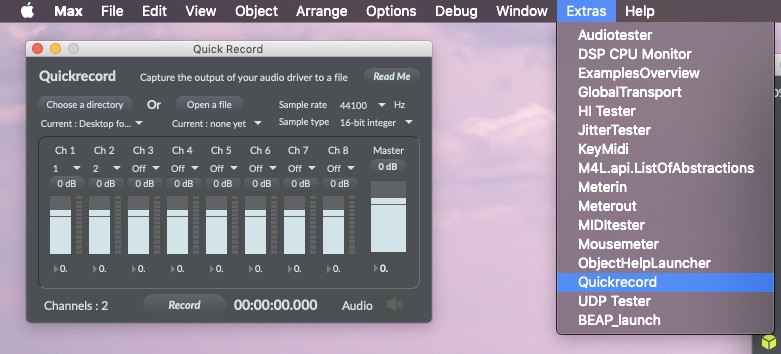
The last feature I wanted from this patch was the option to record the the mix being created in Logic Pro X or any DAW Soundflower is an audio driver, created by Cyling74, which can be used to route audio between different computer applications by creating a virtual audio interface (Lee, 2013). Soundflower is a useful tool to have installed on your system, however, I have found on my computer there is a compatibility issue. All audio becomes glitchy once Soundflower is activated and any recordings made will have these glitches. Unable to find a fix, which is likely due to the age of the driver, the best alternative is already built into Max. Max has a quick record function which allows you to record from selected audio outputs (Cycling’74, 2011) (see Fig.5.10.). Once your session has been recorded you can import the audio file into any DAW.
My Computer – Mac Mini (late 2014) running macOS Mojave 10.14.4 with Focusrite Scarlett 2i4 2nd generation audio interface.
References.
Admin, 2018. Soundflower for macOS Mojave (and sierra high sierra). [Online] Available at: https://www.fluxforge.com/blog/soundflower-os-x-10.11-10.12-macOS-sierra/ [24/04/2019].
Cycling’74, 2011. Did You Know #30: Quick Record. [Online Video] Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-PVSSv8nw2w [25/04/2019].
Cycling74, 2019. Scale Reference. [Online] Available at: https://docs.cycling74.com/max7/maxobject/scale [25/04/2019].
Cycling74, 2019. Sending and receiving audio from logic. [Online] Available at: https://cycling74.com/forums/sending-and-receiving-audio-from-logic [24/04/2019].
Lee, H., 2013. Quick Tip: Routing Audio Between Application Using Soundflower. [Online] Available at: https://music.tutsplus.com/tutorials/quick-tip-routing-audio-between-applications-using-soundflower–audio-16199 [24/04/2019].